In today’s competitive business landscape, understanding your customers and fostering positive relationships with them is absolutely necessary. Two acronyms you’ve likely encountered in this context are CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and CEM (Customer Experience Management). While they might seem similar at a glance, they serve distinct purposes in the realm of customer relations and service.

This article aims to demystify CRM and CEM, exploring their differences and intersections, and how to measure performance of each of them to ensure business success.
What is CRM Customer Relationship Management?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) refers to the strategies, technologies, and practices that companies use to manage and analyse customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. The goal of CRM is to improve business relationships with customers, assist in customer retention, and drive sales growth.
CRM systems compile data from various communication channels, including the company’s website, telephone, email, live chat, marketing materials, and social media. Through the CRM approach and the systems used to facilitate it, businesses learn more about their target audiences and how to best cater to their needs.
CRM experience focuses on the administrative and transactional aspects of customer interaction. It’s about managing detailed information about individual customers and all customer ‘touchpoints’ for building customer loyalty.

CRM involves strategies to manage a company’s interactions with potential and current customers, using data analysis about customers’ history with a company to improve business relationships, focusing on customer retention, and ultimately driving sales growth.
What Is CRM Experience?
CRM experience refers to the proficiency and understanding an individual possesses in utilising Customer Service and Relationship Management software and tools. This encompasses a wide range of skills, from the basic ability to input and track customer interactions and data to more advanced competencies such as analysing customer behaviour, segmenting customers for targeted marketing campaigns, and leveraging CRM data to drive sales and improve customer service.
Having Customer Relationship Management experience means that a person is adept at managing customer relationships through technology, understanding the customer lifecycle, and utilising data-driven insights to enhance the customer experience. In a job context, CRM experience is highly valued as it directly impacts a company’s ability to attract, retain, and satisfy its customers, thereby driving growth and profitability.
What Is CEM Customer Experience Management?
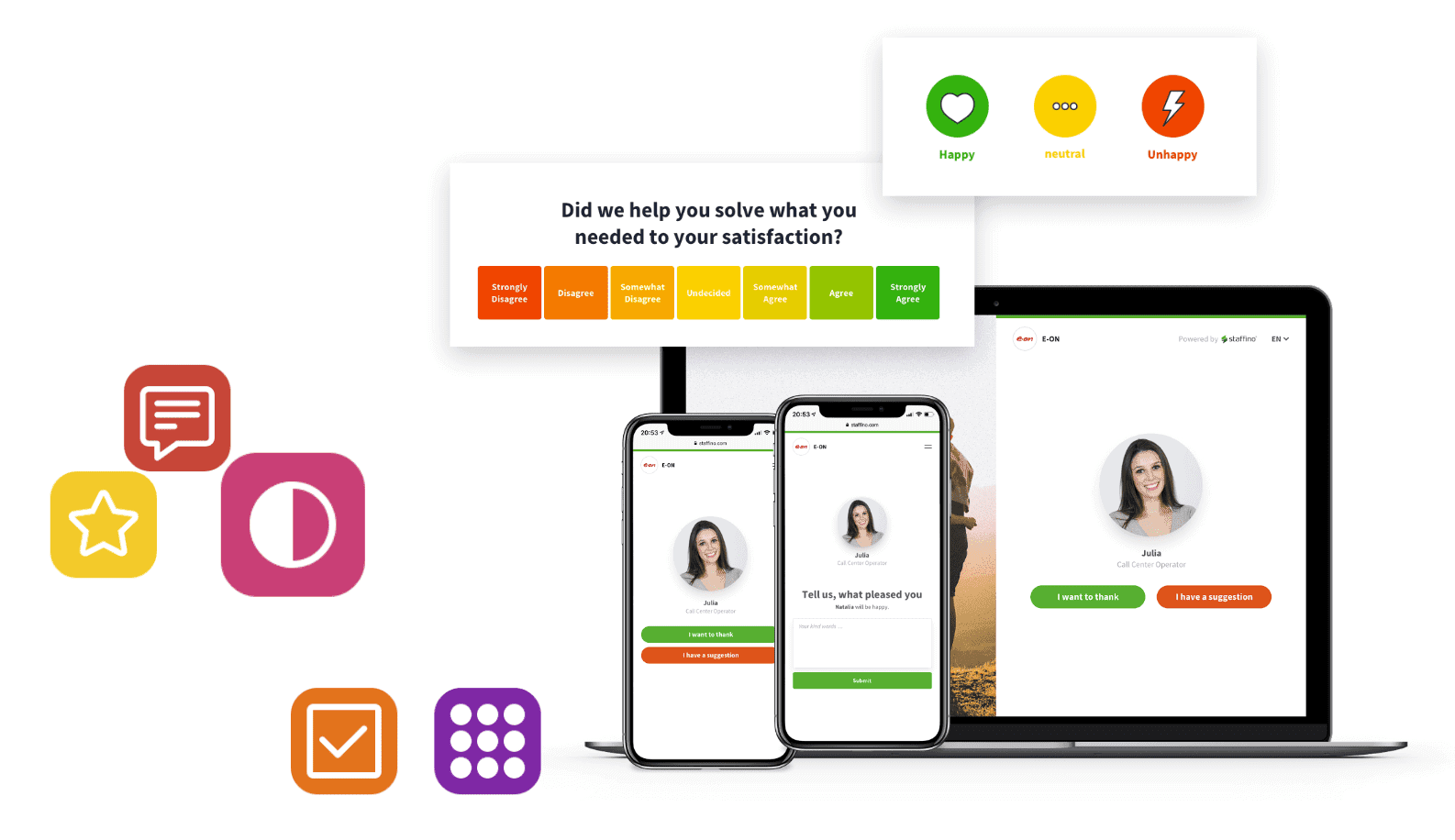
Customer Experience Management (CEM or CXM) is the process of designing and responding to customer interactions to meet or exceed customer expectations, thereby increasing customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy.
CEM is a strategy that focuses on creating a unified customer experience across all touchpoints and phases of the customer journey. CEM meaning in business goes beyond the transactional nature of CRM to encompass the emotional journey of the customer.
CEM customer experience aims to manage and influence customer perceptions, shaping the entirety of the customer’s journey with a brand. This includes every interaction, from initial awareness through to post-purchase support and beyond. A key role within this strategy is that of the CEM customer experience manager, who oversees the development and implementation of the practices and environments that customers interact with.

Transform Your Customers' Experiences
Create a bulletproof customer journey with tailored CX products and services that will foster loyalty and reduce churn.
Customer Relationship Management vs Customer Experience Management
CEM and CRM both aim to foster positive relationships between businesses and their customers. However, they focus on different aspects of the customer-business relationship.
- CRM is more focused on the systematic and strategic management of customer information and interactions.
- In contrast, CEM prioritises the customer’s subjective experience and emotional connection with the brand.
Customer Relations vs Customer Service

What’s the deal with customer relationship management and customer service? CRM can be seen as aligning more with customer service, focusing on the resolution of immediate issues and the management of customer relations. CEM, however, encompasses the entire spectrum of customer relations and service, aiming to create memorable and positive experiences that foster brand loyalty.
The Role of Data in CRM and Customer Experience Management
Both CRM and CEM rely on data to inform their strategies, but the type of data and how it’s used differs. CRM focuses on quantitative data (e.g., purchase history and customer demographics) to tailor customer relations and service strategies. CEM, on the other hand, also considers qualitative data (e.g. feedback from customer surveys and sentiment analysis) to gauge the emotional impact of the customer experience.
Objective vs Subjective Metrics
CRM often emphasises objective metrics such as sales figures, customer lifetime value, and customer churn rates. CEM, meanwhile, puts a spotlight on subjective metrics like customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy. Both sets of metrics are crucial for a comprehensive understanding of a business’s performance but from different angles.
Integrating CRM and CEM
While CRM and CEM have distinct focuses, they are not mutually exclusive. Integrating CRM and CEM strategies can provide a holistic approach to managing customer relationships and experiences. By leveraging the detailed customer insights from CRM systems to inform and enhance the customer experience strategy (and vice versa), you can create a more seamless, personalised customer journey.
Measuring and Improving Performance of CRM and CEM
Both CRM and CEM involve continuous measurement and improvement of performance. Employee performance management, customer feedback, and performance review mechanisms are essential in both strategies to gauge the effectiveness and identify areas for enhancement. Businesses should strive to measure performance not just in terms of sales and service metrics but also in customer satisfaction and loyalty to ensure a balanced approach to growth. Here are different measurement techniques for customer experience management vs customer relationship management:
CRM Performance Measurement
Sales Metrics: Track metrics such as sales cycle length, lead conversion rate, and customer acquisition cost. These indicate the CRM’s effectiveness in managing sales-related activities.
Customer Retention Rates: Measure how well your CRM strategies retain customers over time. A higher retention rate suggests effective customer retention management and CRM practices.
Customer Satisfaction Scores (CSAT): Use surveys to gauge customer satisfaction with your products or services, indicating the CRM’s success in maintaining positive relationships.
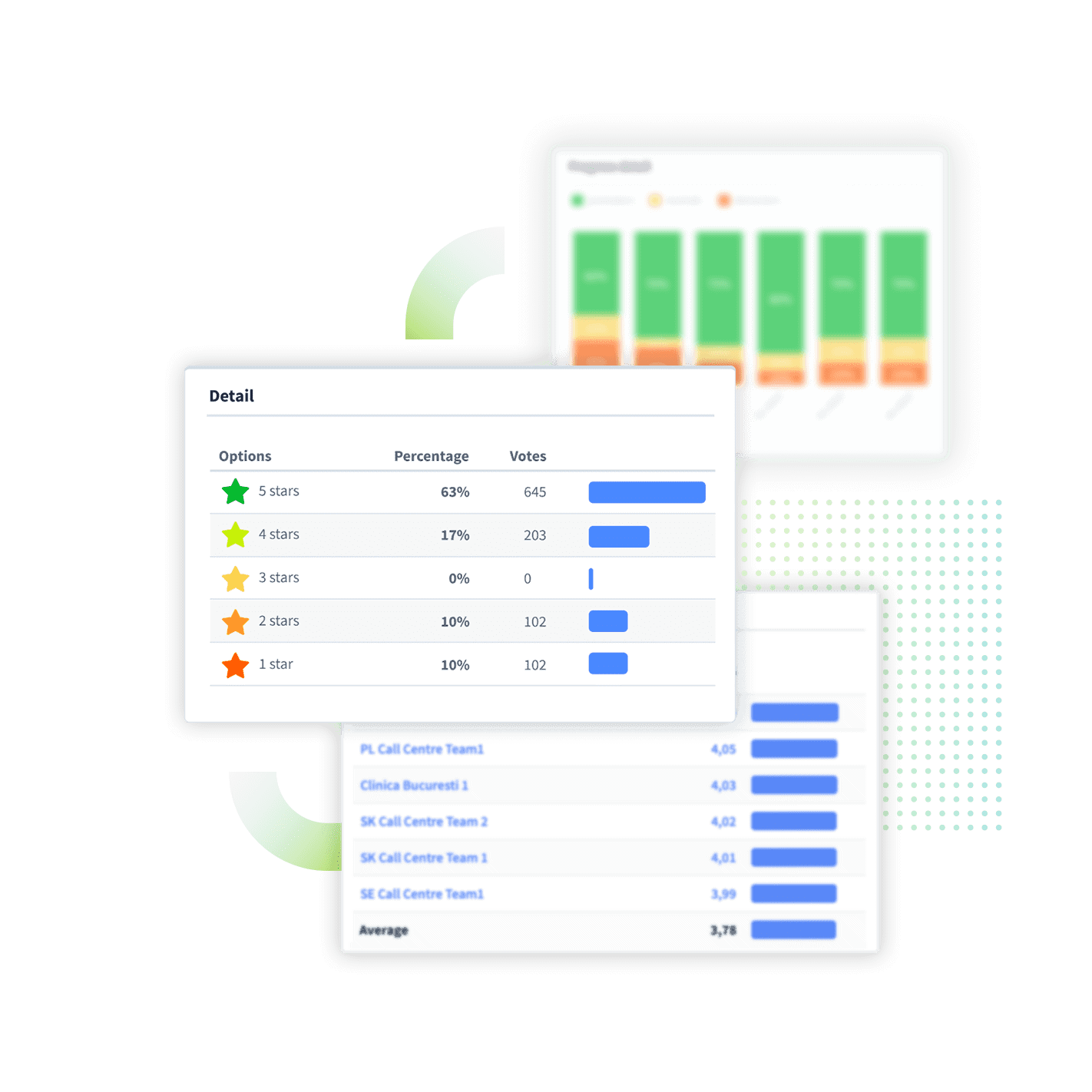
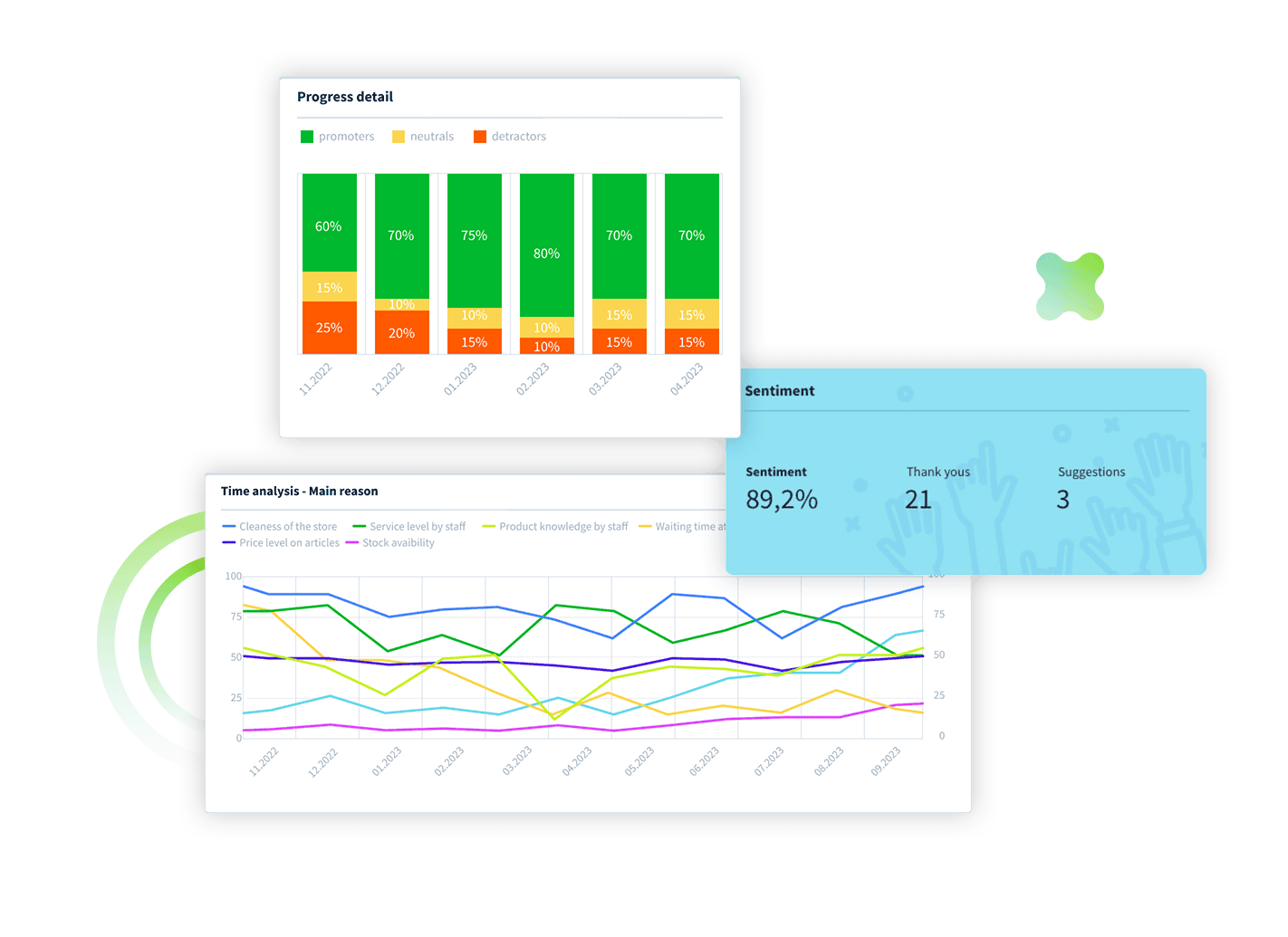
Net Promoter Score (NPS): This measures customer loyalty (percentage of NPS promoters) and the likelihood of them recommending your business to others, reflecting the CRM’s impact on customer perceptions.
Email Marketing Performance: Analyse open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates from email campaigns managed through the CRM system.
Revenue Growth: Assess the CRM’s impact on revenue by looking at metrics such as average revenue per user (ARPU) or revenue growth from existing external customers.

Boost Customer Experience with NPS, CSAT & CES
Get the most accurate and actionable insights into your customer satisfaction with Staffino's CX metrics. With automated surveys and effective reporting, you can quickly gain valuable insights into your customer journey.
CEM Performance Measurement
Customer Effort Score (CES): Measure how easy it is for customers to interact with your business, indicating the effectiveness of your CEM in reducing customer effort.
Customer Journey Analytics: Analyse data across various touchpoints to understand customer behaviors and preferences, identifying areas for improvement in the customer experience.
Voice of the Customer (VoC) Programs: Collect and analyse CX feedback across different channels to gauge overall satisfaction and identify specific issues or areas for enhancement.
Online Reputation Management: Monitor social media mentions, reviews, and ratings to understand public perception and the impact of your CEM strategies.
Employee Engagement and Feedback: Since employees play a crucial role in delivering customer experiences, measure their engagement and collect their feedback on customer interactions.
Churn Rate: Calculate the percentage of customers who stop doing business with you over a certain period. A lower churn rate indicates more effective CEM practices.
Time to Resolution: Track the average time it takes to resolve customer issues or inquiries, with shorter times typically indicating better customer experience management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while CRM vs CEM serve different purposes, they are complementary strategies that, when integrated, can significantly enhance customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy. Understanding the nuances between customer relationship management and customer experience management allows you to adopt a more comprehensive approach to customer engagement and employee performance. By focusing on both the systematic management of customer relationships (CRM) and the holistic crafting of the customer experience (CEM), you can ensure your company not only meets but exceeds customer expectations.

Get a First-Hand Experience Today!
Staffino is the perfect tool for creating engaging surveys, tracking performance, responding to customer feedback, and rewarding top employees. Get started today with our FREE demo!









